Web Socket
WebSocket is bidirectional, a full-duplex protocol that is used in the same scenario of client-server communication, unlike HTTP it starts from ws:// or wss://. It is a stateful protocol, which means the connection between client and server will keep alive until it is terminated by either party (client or server). After closing the connection by either of the client and server, the connection is terminated from both ends.
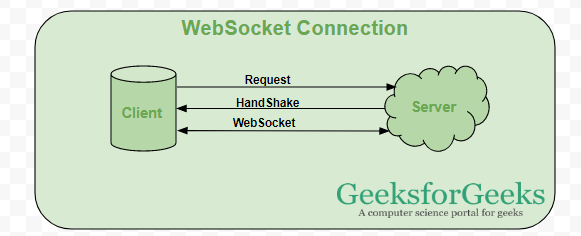
Let’s take an example of client-server communication, there is the client which is a web browser and a server, whenever we initiate the connection between client and server, the client-server made the handshaking and decide to create a new connection and this connection will keep alive until terminated by any of them. When the connection is established and alive the communication takes place using the same connection channel until it is terminated.
This is how after client-server handshaking, the client-server decide on a new connection to keep it alive, this new connection will be known as WebSocket. Once the communication link establishment and the connection are opened, message exchange will take place in bidirectional mode until connection persists between client-server. If anyone of them (client-server) dies or decide to close the connection is closed by both of the party. The way in which socket works is slightly different from how HTTP works, the status code 101 denotes the switching protocol in WebSocket.
When can a web socket be used:
- Real-time web application: Real-time web application uses a web socket to show the data at the client end, which is continuously being sent by the backend server. In WebSocket, data is continuously pushed/transmitted into the same connection which is already open, that is why WebSocket is faster and improves the application performance.
- For e.g. in a trading website or bitcoin trading, for displaying the price fluctuation and movement data is continuously pushed by the backend server to the client end by using a WebSocket channel.
-
Gaming application: In a Gaming application, you might focus on that, data is continuously received by the server, and without refreshing the UI, it will take effect on the screen, UI gets automatically refreshed without even establishing the new connection, so it is very helpful in a Gaming application.
-
Chat application: Chat applications use WebSockets to establish the connection only once for exchange, publishing, and broadcasting the message among the subscribers. It reuses the same WebSocket connection, for sending and receiving the message and for one-to-one message transfer.
When not to use WebSocket:
WebSocket can be used if we want any real-time updated or continuous streams of data that are being transmitted over the network. If we want to fetch old data, or want to get the data only once to process it with an application we should go with HTTP protocol, old data which is not required very frequently or fetched only once can be queried by the simple HTTP request, so in this scenario, it’s better not use WebSocket.
RESTful web services are sufficient to get the data from the server if we are loading the data only once.
Differences between HTTP and WebSocket Connection:
| Feature | WebSocket | HTTP Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Communication | Bidirectional | Unidirectional |
| Protocol | WebSocket | HTTP |
| Format | ws:// or wss:// | http:// or https:// |
| Connection Type | Persistent | Non-persistent |
| Usage | Real-time applications | RESTful applications |
| Data Transmission | Can send data from client to server or vice versa | One-way transmission from client to server |
| Connection State | Connection kept alive until terminated | Connection closed after each request |
| Speed | Faster than HTTP connection | Slower compared to WebSocket |
| Example Usage | Trading, monitoring, notification services | Simple RESTful APIs |