Parallel Computing
Introduction
1 Laying Bricks
- lay faster
- use a machine
- hire more people
Analogy
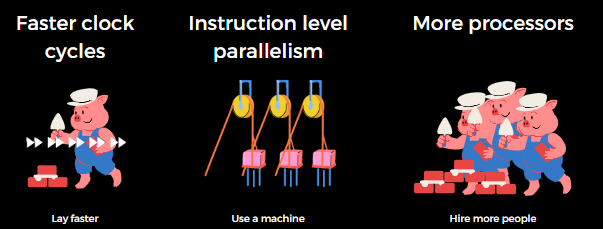
- faster clock cycles
- instrcution level parallelism
- more processors
2 Software Parallelism
- subset of concurrency
What is software parallelism?
- Divide the work into units of tasks.
- Run independently.
- No dependencies from other tasks.
- Can be executed simultaneously
3 Data-Parallel Primitives (DPP)
- building blocks
- commonly used patterns
- combined to create complex parallel algorithms
- reuse existing high performance implementations
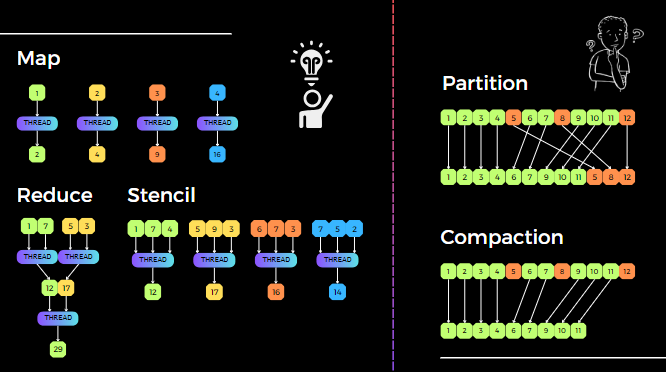
Common Types of DPP
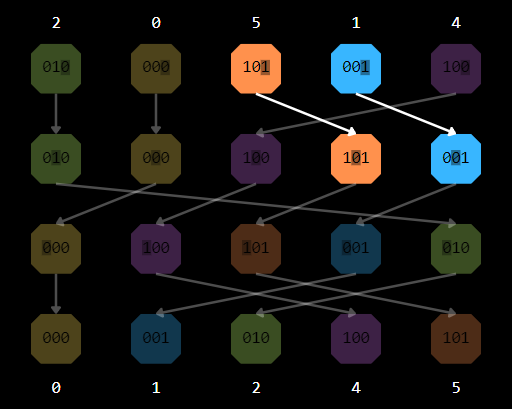
Map, Stencil, Reduce, Scan, Gather/scatter, Compaction, Partition
- Sum Scan
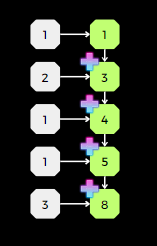
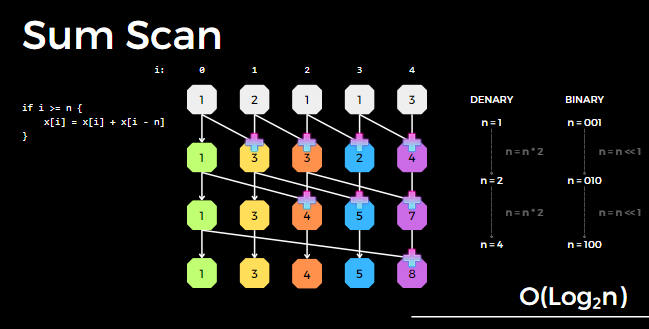
Big O Notation-Please explain O(log2n)
- Compaction
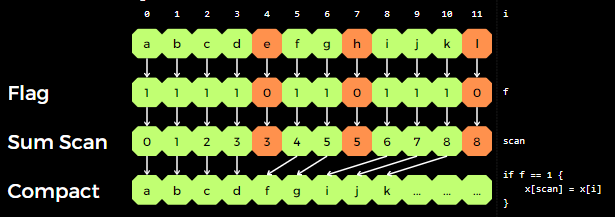
- Partition
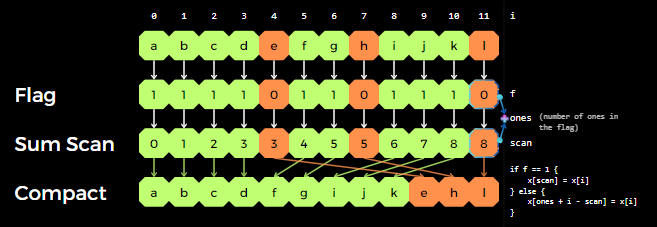
- Radix Sort
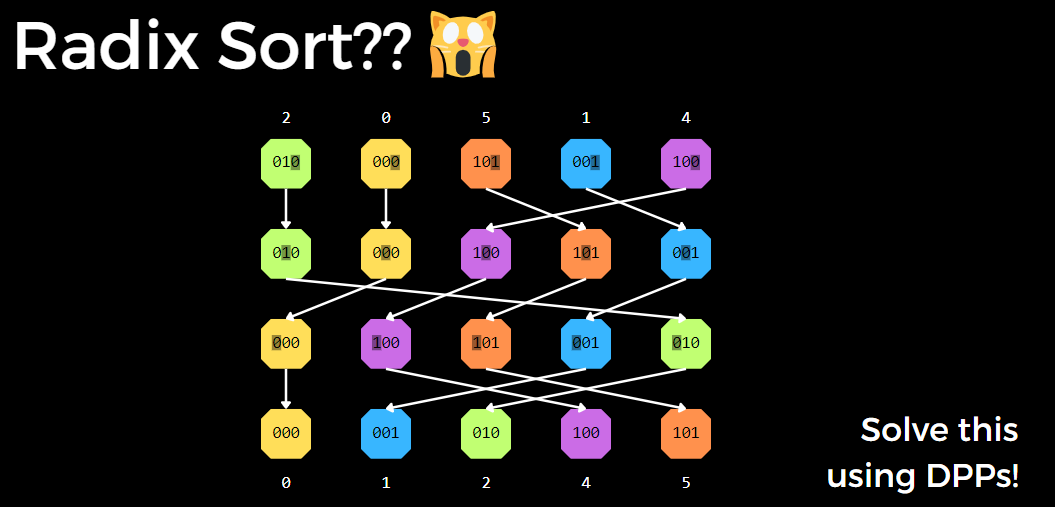
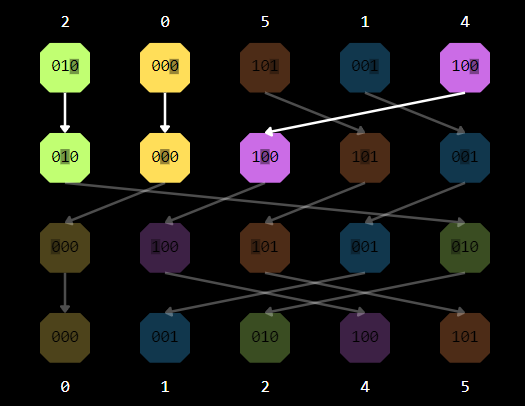
4 Conclusion
- Thread count (hardware is still important)
- Write/mutate data (utilize atomics if necessary)
- Graph coloring
- A graph coloring is an assignment of labels, called colors, to the vertices of a graph such that no two adjacent vertices share the same color.
- Memory is slow
- Beware of branching
- Data structures
- Use DPP to express your algorithm
